1. What is Synology High Availability?
The term "high-availability" refers to a server layout solution designed to reduce service disruptions caused by server failures. Synology High Availability (SHA) deploys two servers to form a "high-availability cluster," with one server acting as the "active server" and the other serving as the standby "passive server."
In a high-availability cluster, data from the active server is continuously replicated to the passive server, so there is a mirrored copy of all the files in both servers. In this way, in the event of an active server corruption or failure, the passive server can take over all services, minimizing the time of system service interruption.
2. Please read the following sections carefully before attempting to create a high-availability cluster.
Hardware requirements:
SHA requires two identical Synology servers as active and passive servers.
Two different Synology servers can function as active and passive servers, but with limitations.
system requirement:
Active and passive servers must be the same model and both support Synology High Availability.
The same version of DSM must be installed on both servers.
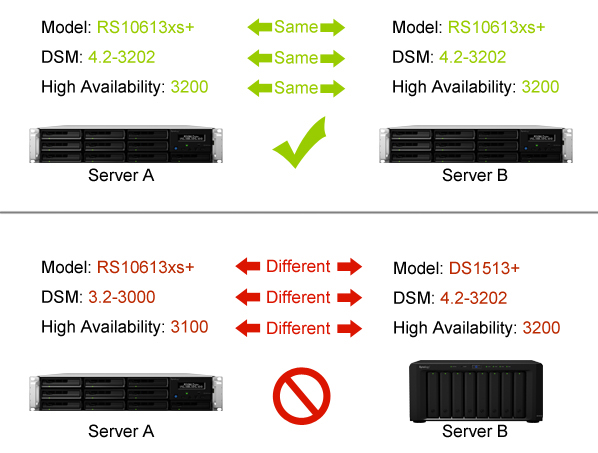
Note: The above figure is for reference only. Your model and DSM version may vary.
Volumes and hard drives:
The hard drives of both servers must be identical in size to avoid data inconsistencies.
Both active and passive servers must have the same number of hard drives. In addition, the location of the hard disk must be the same.
Neither server can contain any volumes in SHR format. Go to the Storage Manager > volume to make sure there are no SHR volumes.
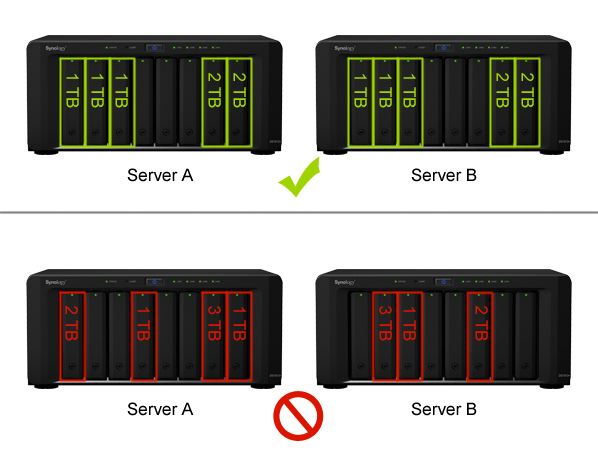
注:上圖僅供參考。您環境中的硬盤數量和大小可能不同。
Web environment:
Both servers must be assigned a static IP address. Make sure that the IP addresses of both servers are accessible and belong to the same subnet, otherwise an error may occur when initializing the transition to the passive server. To change the network settings, log in to each server and go to Control Panel > Network > Network Interface, select the network interface and click Edit.
Both servers must have the same number of LAN ports. If both servers are equipped with more NICs, these NICs will be treated as additional LAN ports.
Synology High Availability does not support: proxy server, DHCP, DHCP server, IPv6, PPPoE, and Wi-Fi. Be sure to turn off all of the above features before creating a high-availability cluster.
Note: Once a high-availability cluster is created, the SSH and NTP servers are automatically created on the active server.
3. Connect to the server
This section describes how to connect two servers to create a high-availability cluster. Please refer to the following steps:
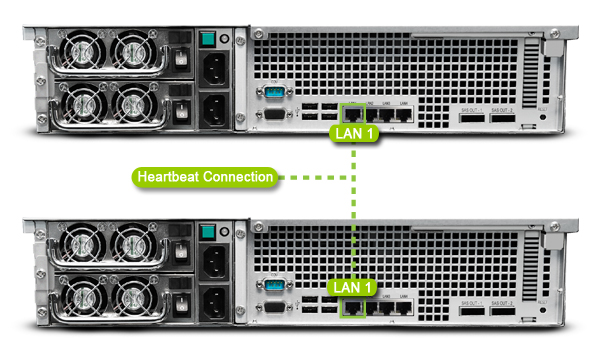
1>> Please use a network cable to connect the two servers to each other. This connection acts as a "Heartbeat" connection between the two servers to speed up communication and copy data from the active server to the passive server. This connection must meet the following conditions:
The same network interface is used on both servers. For example, if one end is connected to the server's LAN 1 interface, the other end must also be connected to the LAN 1 interface of the other server.
Both servers use the fastest network interface. If both servers are configured with a 10GbE add-on NIC, the NIC must be used for the connection.
A direct connection between the two servers without going through any switches or routers.
2>>Use a network cable to connect the two servers to the remaining network interfaces. Please confirm that these connections are valid and all belong to the same network.
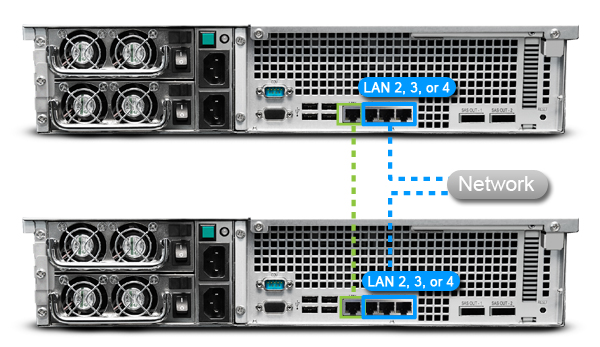
Note: To prevent service disruption due to network failure, we recommend deploying multiple switches in your network environment to enable each server in a high-availability cluster to connect to a separate switch.
3>> Servers can now be combined into a high-availability cluster. Please follow the steps below to continue.
4. Consolidate servers and create high-availability clusters
Once the two servers are properly connected, you can combine them into a high-availability cluster by following the steps below.
1>>Log in to the server where you want to act as an active server for accounts belonging to the administrators group.
2>>Open High Availability Manager.
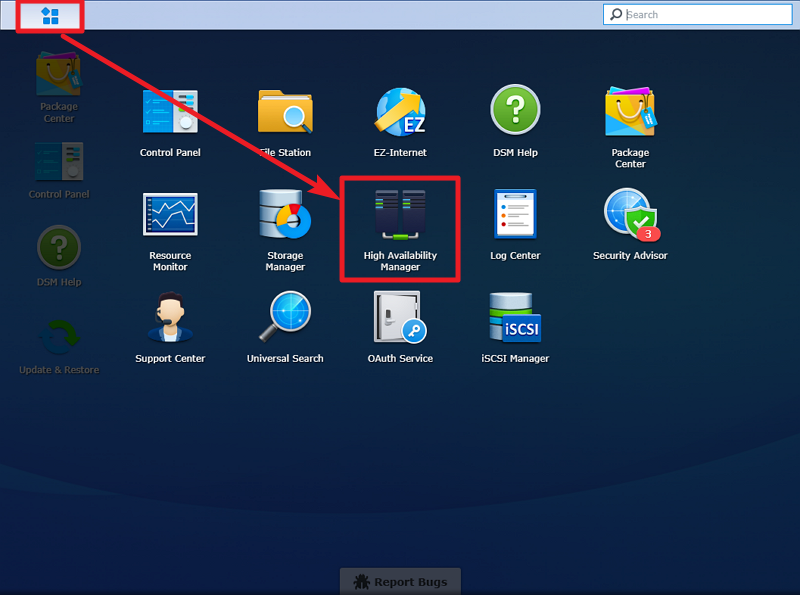
3>>Click Create HA Cluster to launch the setup wizard.
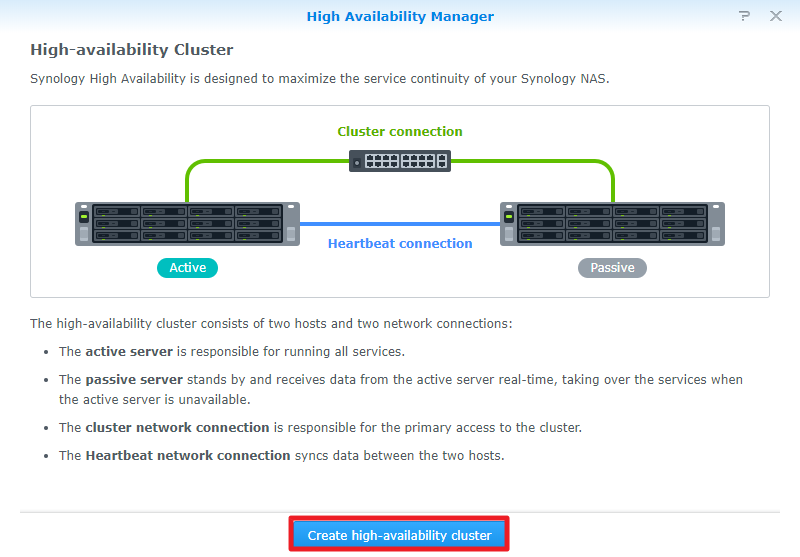
4>>Click Next.
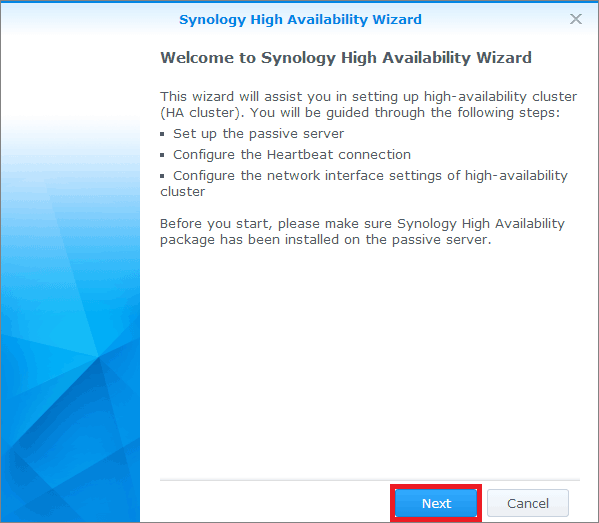
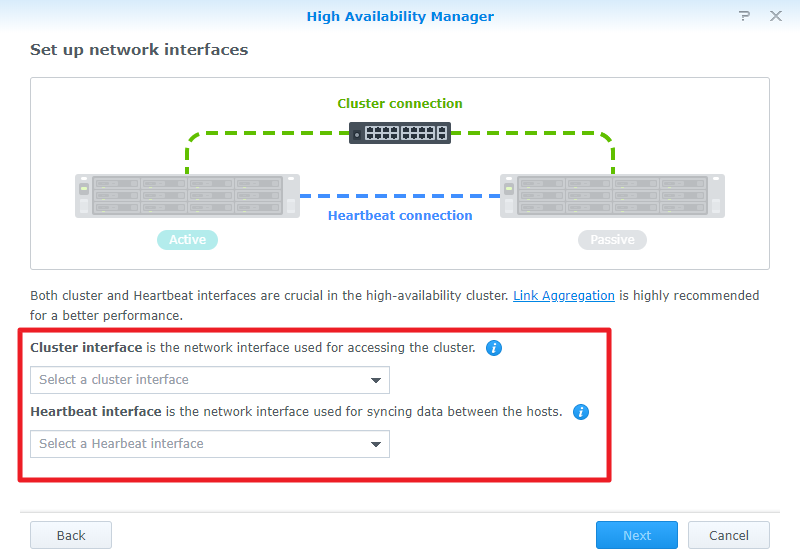
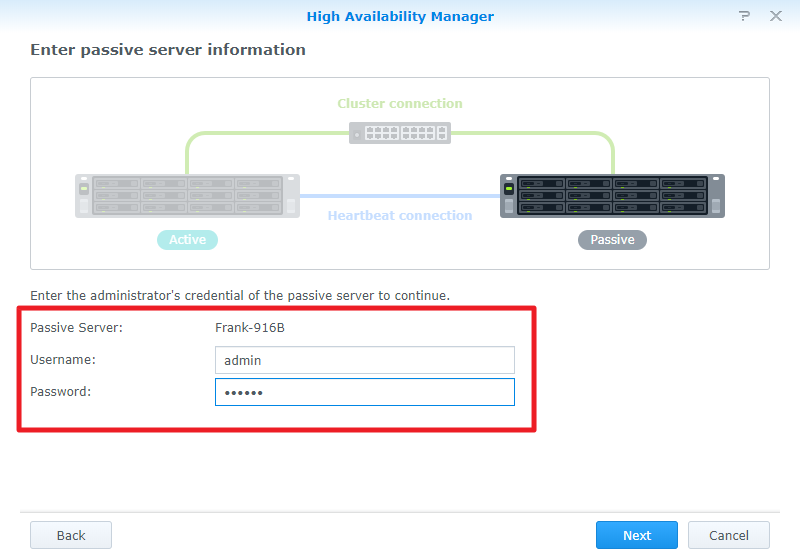
5>>Specify the IP address, domain username, and password that you want to use as a passive server. (To find the IP address, log in to another server and go to Control Panel > Network > Network Interface. Remember to verify that both servers use a static IP address.) Then click Next.
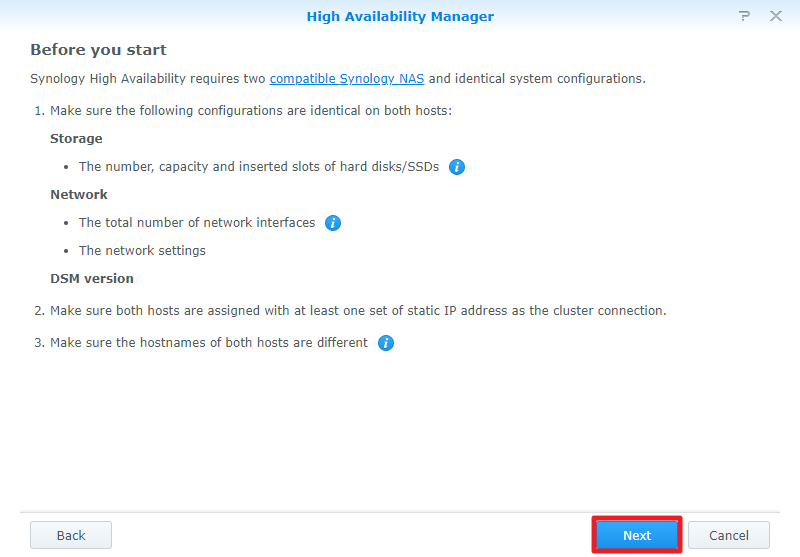
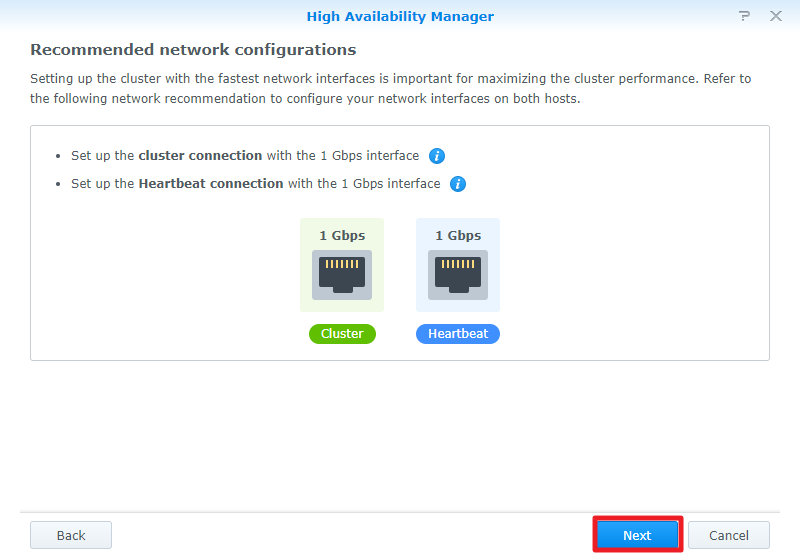
Select the network interface to use for the high-availability cluster Heartbeat connection. (This option should be the same as the network adapter you use to connect the two servers to each other.) Then click Next.
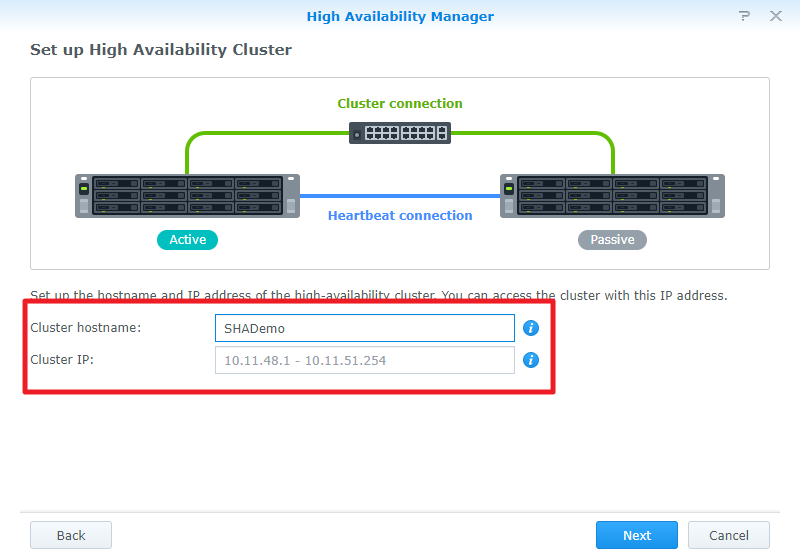
Specifies the name of the high-availability cluster. Also, select the network interface to connect to the data network and then specify the IP address and subnet mask for the high-availability cluster. You can access the high-availability cluster resource with the name and IP address specified here. Then click Next.
Confirm the settings. Then click Apply.
The setup wizard will begin to create a high-availability cluster. The creation time varies depending on the system environment.
When you are done, you will see the cluster status in the overview page.
5. Resolve the issue after a failure
When certain errors occur, the system automatically transfers the service from the active server to the passive server. This situation is called "failover." The system may initiate a failover under the following conditions.
5.1 Damaged storage space
The storage space on the active server (for example, storage volume, iSCSI LUN) is in a corrupted state, but the failover occurs when the corresponding storage space on the passive server is functioning properly. For example: if server A is the active server and server B is the passive server. When the storage space on Server A is corrupted but the corresponding storage space on Server B is still good, the system performs a failover.
Note: If there are no volumes or iSCSI LUNs (paragraph chunking) on the corrupted storage space, the system does not initiate a failover.
After the failover process is complete, do the following:
1>>Go to the hard drive status page and identify the missing or corrupted hard drive on Server A (now a passive server).
If a hard drive is missing, install the hard drive in the appropriate slot so that both servers have the same number of hard drives.
If there is a damaged hard disk, please replace it.
2>> Verify that both servers have the same hard disk configuration and that all hard disks are in a normal or uninitialized state.
3>>Go to the Storage Status page and click Repair to repair the storage space.
5.2 Service Error
A failover occurs when there is an error in the monitored service. For example: If the service monitored on Server A (Active Server) fails, the system will fail over to Server B. In this case, do the following after the failover is complete.
1>>Go to the overview page.
2>> Server A should now be a passive server, click Manage > Close Passive Server.
3>> Server A starts again after it is closed.
5.3 Power failure
Failover occurs when the active server is shut down, restarted, two power components fail, or an external power supply is lost. For example: If Server A is the active server and its power supply fails, the system will fail over to Server B. After the power is restored, turn on Server A (which is now a passive server).
6. Maintain high-availability clusters
To understand the routine maintenance procedures, please see the instructions below.
Program | Description |
|---|---|
Move the two servers to another location |
|
Upgrade RAM or NIC on both servers |
|
Replace a failed component (such as a RAM, fan, or NIC) on a passive server |
|
Replace a failed component (such as a RAM, fan, or NIC) on the active server |
|
Switch the active server to a passive server |
|
Cancel the binding of passive servers to clusters |
|
Bind a new passive server |
|
Remove the high-availability cluster and restore the server to a standalone state |
|
Update system |
|
